Zeppelin L 30(LZ 62)

Description
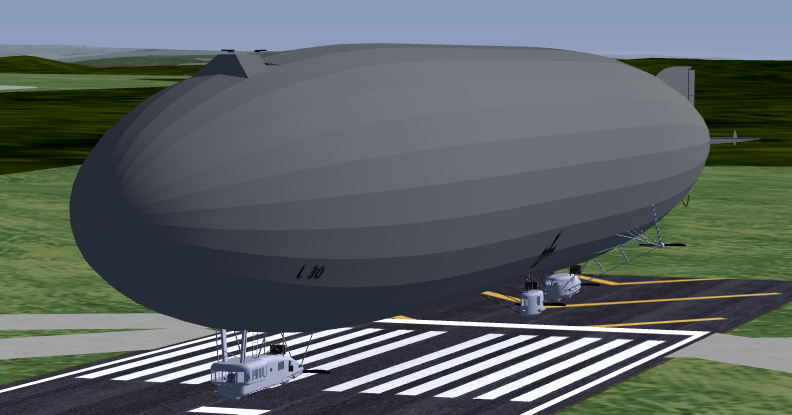
Zeppelin "L 30" (factory number "LZ 62") was the first R-class "Super Zeppelin" of the German Empire. It was the most successful airship of the
First World War with 31 reconnaissance flights and 10 bombing runs carrying a total of 23,305 kg of bombs, with the first ones targeting England,
and the four final raids targeting Livonia and Ösel (Saaremaa). It was at the time of construction the world's largest Zeppelin, and with its
6 engines, "L 30" could reach speeds higher than 100 km/h, making it also the fastest Zeppelin.
It was constructed at Luftschiffbau Zeppelin in Friedrichshafen, the first with gondolas on the sides. It remained in the service of the Imperial
German Navy from 1916 to its decommissioning in 1917. "L 30" was decommissioned in 1917, and survived World War I. It was handed over to Belgium
as part of the war reparations laid on Germany. Its gondolas are today on display at the Royal Military Historical Museum in Brussels, the only
remaining gondolas of a war Zeppelin in the world.
- Length: 198 m (649 ft 4 in)
- Diameter (max.): 23.9 m (78 ft 4 in)
- Gas volume: 55,000 m3 (1,949,600 sq ft)
- Number of gas cells: 19
- Number of gondolas: 4
- Number of propellers: 6 x Lorenzen
- Number of crew members: 17
- Max speed: 103 km/h (28,7 m/s; 62.2 mph)
- Range: 7,400 km (4600 miles)
- Max altitude: 5300 m (17,400 ft)
- Payload: 27,721 kg (61,600 lb)
- Empty weight: 36,186 kg (79,600 lb)
- Engines: 6 x Maybach HSLu of 240 hp each. Total: 1440 hp.
- Factory number: LZ 62
- Type: R
Download
Zeppelin L 30(LZ 62) Size 8.9Mb
Pilot Notes
Gas valve controls
- F/f - Open/close the gas valves of the fore gas cells.
- G/g - Open/close the gas valves of the aft gas cells.
Rigid airships like L 30 take-off light in a static maneuver and normally land weighed-off to slightly heavy in a static maneuver. The primary use for the gas valves is to reduce static lightness when needed.
Ballast controls
- w - Show current on-ground weight. Only works when on the ground.
- W - Weigh off to neutral by adding/removing ballast. Takes about 10 seconds and is only applicable when on the ground.
- E/D - Drop one quick-release (a.k.a. emergency) ballast bag fore/aft. There are 6 bags fore and 4 aft.
- d - Drop all quick-release ballast bags from the trim ballast.
- Ctrl+W - Refill the quick-release ballast bags from the trim ballast.
Ground crew
- Y - Tell ground crew to let go.
- U - Request ground crew to prepare for landing.
- Ctrl + click on terrain - Place the ground crew.
Weapons
- b - Open/close bomb bays.
- j - Select next Bomb.
- J - Drop selected Bombs.
- r - Fire MG.
Specials
- B - Open/close observer car bays.
- n - Raise observer car.
- N - Lower observer car.
- o - Use oxygen masks at high altitude.
- k - Start automatic landing sequence, you must be lower than 200 m for that.
Engine Controls
Engines are controlled with the "Machine Telegraph".
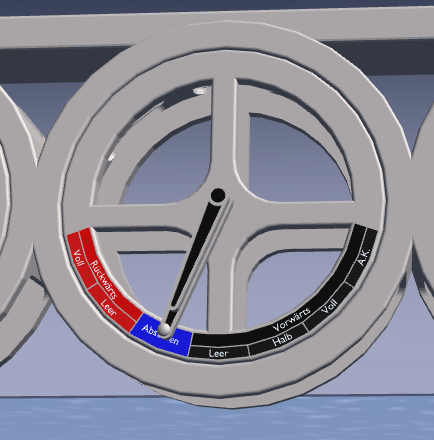
There is no need for the usual key commands. To start the engine just click on the "Leer" text left to the lever. The left
part of the lever will jump into position. When the command is executed (Engine started or throttle changed) the right part
of the lever will jump into position.
Engines are arranged from left to right, the fore engine is on the far left, then comes the left side engine, next comes then
right side engine and finally the three aft engines.
Back